The consideration of acoustics and aeraulics in a construction project is necessary in relation to different works trades: architectural, technical, not to mention the envelope.
With regard to related issues, SILDIS® software makes it possible to easily, quickly, and reliably perform Computer Aided Design tasks.
All calculations are possible taking into account contextualized thermodynamic conditions:
- for ambient air (e.g. for ordinary applications in the building sector with the exception of those related to exhaust gases, involving high temperatures, for which calculations are also possible)
- as required for simulations in the context of industrial construction projects (possibly with fluids other than air and with extreme temperature and pressure conditions)
In terms of acoustics, the frequency range considered for single frequency simulations is 20 Hz - 20 kHz, the performance indicators being provided in bands of 1/3 octave, 1/1 octave and in the form of a unique index with respect to a reference sound spectrum (e.g. αw, Rw).
The fact that the software is in Excel format, with drop-down menus and with the possibility of selecting materials from libraries [1] makes it a practical tool for various participants in the construction process: project managers, architects, consultants, technicians and engineers from design offices (acousticians, specialists in aeraulics and fluids) and manufacturers Research and Development (R&D) centers. SILDIS® can be used, depending on the context, in the field of construction as in the industrial sector:
- to carry out calculations as part of engineering missions, allowing modeling in terms of predictive acoustics and sizing of soundproofing equipment
- to prepare and optimize laboratory measurement campaigns, by pre-selecting configurations worthy of interest as part of the development of acoustic insulation or rooms reverberation control products and systems, or of silencers SILDIS® offers a virtual acoustics laboratory environment)
Limitation of noise transmission in ducts
The software allows the prediction of the insertion loss, of the self noise and of the total pressure loss of elements of aeraulic networks whose impact, in the event of accumulation, is calculated:
- silencers [6], either resonant or dissipative (i.e. with absorbent lining, possibly multilayered). The calculations are possible by combining plates (e.g. steel, aluminum) [4] possibly perforated, porous materials (glass wool, rock wool, basalt wool, polyester or based on ceramic fibers wools, foams) [3] and facings (cloths, fabrics) [5]
- straight lengths, elbows, nozzles
The components of the air network can be of rectangular, square or circular cross section.
For a silencer, the results of the calculations are comparable with the standardized measurement: see NF EN ISO 7235 Acoustics - Laboratory measurement procedures for silencers in ducts and terminal units - Insertion loss, flow noise and total pressure loss.
|
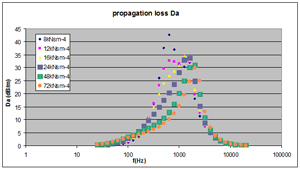
Example of the dependence of the acoustic performance of a dissipative silencer on the airflow resistance of its lining, in terms of longitudinal attenuation aka propagation loss (dB/m), as can be evaluated with the SILDIS® software |
Cf. Module(s) 1 / 1+ /1A
Cf. Module(s) 1B
Cf. Module(s) 3
Cf. Module(s) 4
Cf. Module(s) 5, 5A
Cf. Module(s) 6
Cf. Module(s) 7
Cf. Module(s) 8
Cf. Module(s) 8B, 8C, 8D, 8E
>> Acoustics - Boosting silencer performance
>> Design and calculations of high performance baffle (splitter) silencers
>> Noise attenuation - Cylindrical dissipative silencer with reduced pressure drop
>> Modeling of the propagation and attenuation of noise in aeraulic networks with SILDIS® software
>> Acoustics - simulation software SILDIS® – silencers sizing online
>> Silencers - Modeling the acoustic behavior of curved absorbers
>> Sizing of reactive silencers with non-perforated tubes with the simulation software SILDIS®
Sound transmission through partitions
The software allows the prediction of the sound reduction index of walls, possibly multilayered, for sound insulation:
- constituting the envelope of buildings: walls, slabs, roofs or subject to interior carpentry work (e.g. metal or wood joinery) and plastering: partitions, ceilings, linings, not to mention industrial acoustic insulation panels, screens (noise barriers) and also components of glass doors and frames
- constituting the envelope of silencers inserted in ventilation and air conditioning networks or in chimneys
Calculations are possible by combining plates (e.g. concrete, plaster, wood, steel, aluminum, glass) [2], possibly joined together, and porous materials (glass wool, rock wool, basalt wool polyester or ceramic fiber based wool, foams) [3].
The plates can be plane, orthotropic (i.e. with corrugations), perforated, with or without a bonded viscoelastic damping layer (e.g. septum, PVB): extensional or constrained (between 2 plates: sandwich panels).
The results of the calculations are comparable to the standard measurement: cf. NF EN ISO 140-3 Acoustics - Measurement of sound insulation in buildings and of building elements - Part 3: laboratory measurement of airborne sound insulation of building elements.
|
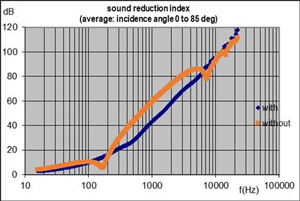
Sound reduction index of a double wall, consisting of a steel plate (1 mm thick) and an aluminum plate (2 mm thick), with - this is then called corrugated sheet - or without corrugations, separated by a porous medium (e.g. wool, mineral or other) with a resistivity of 12.5 kNsm-4, porosity 0.95. For the frequency of 500 Hz, the sound reduction index reaches 27.5 dB with the corrugations, against 43.0 dB without the corrugations, what illustrates (if the frequency of 500 Hz is what one is focusing on), a considerable variation in performance. |
Cf. Module(s) 2 / 2+
Sound absorption
The software allows the prediction of the sound absorption coefficient of linings, possibly multilayered, for the limitation of the reverberation of premises:
- constituting ceiling tiles and suspended baffles, wall panels, laggings, not to mention industrial sound insulation panels, screens (noise barriers) and dividers
Calculations are possible by combining plates (e.g. plaster, wood, steel, aluminum) [4] possibly perforated, porous materials (glass wool, rock wool, basalt wool, polyester ceramic fibers based wool, foams) [3] and facings (cloths, fabrics) [5]
The results of the calculations are comparable to the standard measurement: cf. NF EN ISO 354 Acoustics - Measurement of sound absorption in a reverberation room and also standard ISO 10534-1 Acoustics - Determination of the sound absorption coefficient and impedance in impedance tubes - Part 1: Method using standing wave ratio.
|
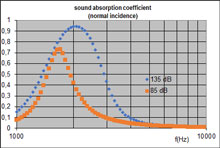
Illustration of non-linearity of the response of a micro-perforated plate to sound excitation: acoustic absorption coefficient under normal incidence (with a ratio circular perforations diameter to thickness being 1, a porosity being 2 %, a cavity depth 0.01 m, a scanning sinusoidal source with a level of 85 dB or 135 dB (accoutning reflections on the sound absorbing lining) |
Cf. Module(s) 2 / 2+
>> Silencers - Modeling the acoustic behavior of curved absorbers
Sound propagation inside rooms
The software allows the prediction of the reverberation time and the sound spatial decay in rooms, for acoustic comfort and noise limitation.
The results of the calculations are comparable with standardized measurement: NF EN ISO 3382-2 Acoustics -Measurement of room acoustics parameters- Part 2: reverberation time in ordinary rooms and NF EN ISO 3382-3 Acoustics -Measurement of room acoustics parameters- Part 3: Open plan offices.
Cf. Module(s) 9, 9A
Sound transmission outside of buildings
The software allows the prediction of sound pressure levels at specified locations.
|
|
Cf. Module(s) 10
Sound propagation outdoor
The software allows the prediction of stacks directivity, of atmospheric sound absorption.
Some of the calculation results are comparable with some input data envisaged in standardized calculation: cf. NF EN ISO 9613-2 Acoustics -- Attenuation of sound during propagation outdoors -- Part 2: General method of calculation.
Cf. Module(s) 8A, 8B
Overall, regarding simulations for acoustics and aeraulics in the construction sector
In the matter of Computer Aided Design (CAD): SILDIS® calculation software for acoustics and aeraulics in the construction sector (in Excel format) is a versatile tool, marketed (with associated training) by Isolation Technologie Services (ITS) in the form of modules, some of which are grouped in packs, according to the needs of users (interface available in French or in English)
The software output data, in terms of simulation of the sound transmission through walls, of sound absorption, of the limitation of noise transmission in ducts, of sound propagation inside rooms and outdoor are useful for many projects, allowing sizing and technical optimization of various construction products and systems, in relation to issues being acoustic comfort and / or soundproofing.
>> SILDIS® software Modules 2 / 2+ Prediction of acoustic performance of plane partitions and walls
>> Acoustics simulation software SILDIS®
>> Acoustics calculation software SILDIS®
>> Design and calculations of high performance baffle (splitter) silencers
>> Noise attenuation - Cylindrical dissipative silencer with reduced pressure drop
>> Modeling of the propagation and attenuation of noise in aeraulic networks with SILDIS® software
>> Acoustics - simulation software SILDIS® – silencers sizing online
>> Silencers - Modeling the acoustic behavior of curved absorbers
>> Room acoustics simulation by ray tracing with ITS
>> Sizing of reactive silencers with non-perforated tubes with the simulation software SILDIS®
[1] the specific characteristics of the materials to be taken into account for the calculations - in addition to the thickness and number of layers, as well as their stacking order - are tabulated
[2] the specific characteristics taken into account are the Young's Modulus, the density, the Poisson factor, the loss coefficient
[3] the specific characteristics taken into account are the resistivity, the porosity, the tortuosity, the thermal characteristic length, the viscous characteristic length, the density
[4] the specific characteristics taken into account are the Young's Modulus, the density, the Poisson factor, the loss coefficient, the installation conditions (free or embedded), and, in the case of perforated plates: the porosity, the geometry of the perforations
[5] the specific characteristics taken into account are the resistance to air flow, the surface mass
[6] the specific characteristics taken into account are the flow rate, the dimensional parameters (e.g. geometry of the internal parts, length)
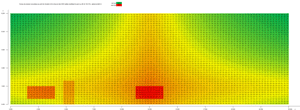 Simulation using Module 10 of the SILDIS® software for predicting sound emissions from buildings and other constructions, of the sound pressure level at a specified location (in the middle of the length of one of the longitudinal facades of a ventilated sound enclosure, with a length 25.0 m, with a height 8.2 m, at 1.5 m from the ground) due to each of the 5000 cells (in this case, with a unit area of 0.04 m2) modeling the wall (dB ref 2E-5Pa - overall A-weighted); the impact of a door (vertical rectangle) and of 2 ventilation silencers (horizontal rectangles) is clearly observable in the lower part of the building wall.
Simulation using Module 10 of the SILDIS® software for predicting sound emissions from buildings and other constructions, of the sound pressure level at a specified location (in the middle of the length of one of the longitudinal facades of a ventilated sound enclosure, with a length 25.0 m, with a height 8.2 m, at 1.5 m from the ground) due to each of the 5000 cells (in this case, with a unit area of 0.04 m2) modeling the wall (dB ref 2E-5Pa - overall A-weighted); the impact of a door (vertical rectangle) and of 2 ventilation silencers (horizontal rectangles) is clearly observable in the lower part of the building wall.